Eye inflammation and light sensitivity often go hand in hand, creating a problematic duo that can disrupt daily life. Understanding their relationship is key to managing symptoms and maintaining eye health. This article delves into the causes of eye inflammation, how it leads to sensitivity to light, and what you can do to alleviate discomfort and protect your eyes.
- Introduction to Eye Inflammation
- Common Causes of Eye Inflammation
- How Inflammation Leads to Light Sensitivity
- Recognizing Symptoms and Seeking Treatment
- Tips for Managing Light Sensitivity
- Protecting Your Eyes from Future Issues
Introduction to Eye Inflammation
Eye inflammation is a common condition that affects people of all ages. The medical term for eye inflammation is uveitis, but it can also include conditions like conjunctivitis and keratitis. These conditions can cause discomfort, redness, and vision problems. Inflammation can be triggered by infections, allergies, or underlying health issues such as autoimmune diseases. The eyes, being delicate organs, are highly susceptible to inflammation, which can affect overall eye health and vision quality.
One of the most interesting aspects of eye inflammation is its ability to cause light sensitivity, also known as photophobia. This sensitivity can be mild, making bright environments uncomfortable, or severe, causing significant pain when exposed to light. According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, up to 90% of people with uveitis experience some degree of light sensitivity. This condition can severely impact one's ability to function in normal lighting conditions, emphasizing the importance of understanding and treating eye inflammation.
The causes of eye inflammation are varied. It can result from bacterial or viral infections, such as herpes simplex virus or cytomegalovirus. Allergic reactions, like those experienced during hay fever, can also lead to inflammation. Additionally, people with autoimmune conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, are at higher risk. Understanding these causes is crucial because effective treatment often depends on identifying and addressing the underlying issue.
Symptoms of eye inflammation can include pain, redness, swelling, blurred vision, and floaters. In some cases, there may be a discharge from the eye, or the eyelids may become swollen. These symptoms may appear suddenly or develop gradually over time. It is essential to seek medical attention if any of these symptoms occur, as untreated inflammation can lead to more serious complications, including permanent vision loss.
Effective management of eye inflammation often involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. Anti-inflammatory medications, such as corticosteroids, are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms. In cases where an infection is present, antiviral or antibiotic medications may be required. Additionally, maintaining good eye hygiene and avoiding known allergens can help prevent flare-ups.
It's fascinating to note that diet can also play a role in managing eye inflammation. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like fish and flaxseeds, have anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit eye health. Similarly, antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables can protect the eyes from oxidative stress, which can contribute to inflammation. Including these foods in your diet can be a simple yet effective way to support eye health.
Understanding eye inflammation is essential for anyone looking to maintain healthy vision. This knowledge can help in early detection and treatment, reducing the risk of complications. Regular eye check-ups are crucial, especially if you have underlying health conditions that put you at higher risk. By staying informed and proactive, you can protect your eyes and enjoy better visual health.
Common Causes of Eye Inflammation
Eye inflammation, medically known as uveitis or conjunctivitis, can stem from various factors. One common cause is infections, which can be bacterial, viral, or fungal. These infections can lead to swelling and irritation of the eye tissues. Bacterial conjuntivitis, for instance, often results from external bacteria entering the eye through dirty hands or contaminated water.
Another significant cause is autoimmune diseases. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus can trigger the body's immune system to unintendedly attack healthy eye cells, causing inflammation. This type of inflammation can be particularly stubborn and may require specialized treatment to control.
Allergies also play a big role. Pollen, dust mites, and pet dander can all cause allergic reactions in the eyes, leading to redness, swelling, and itching. For some individuals, these allergens are unavoidable, making persistent inflammation a chronic issue.
Injuries to the eye are another common culprit. Any kind of trauma, whether it's from a sports injury, a foreign object like dust, or even vigorous eye rubbing, can cause irritation and inflammation. Such injuries damage the delicate tissues in the eye and may require medical intervention to prevent further damage.
Interestingly, prolonged exposure to environmental factors like UV rays and pollutants in the air can also induce eye inflammation. People who spend a lot of time outdoors without proper eye protection are particularly at risk. This highlights the importance of wearing sunglasses and other protective gear to maintain eye health.
"The eyes are more sensitive to environmental toxins than many people realize. It's crucial to understand that what affects our skin can also impact our vision," says Dr. Samantha Green, a renowned ophthalmologist.
Medications too can have side effects leading to eye inflammation. Certain drugs prescribed for conditions like glaucoma or even some antibiotics may cause reactions that result in swelling or redness in the eyes. Patients should always inform their healthcare providers about any unusual symptoms they experience while on medication.
Last but not least, underlying health conditions such as diabetes should not be overlooked. Diabetic patients often experience various eye problems due to high blood sugar levels, contributing to inflammation and sometimes leading to more severe complications if not properly managed.

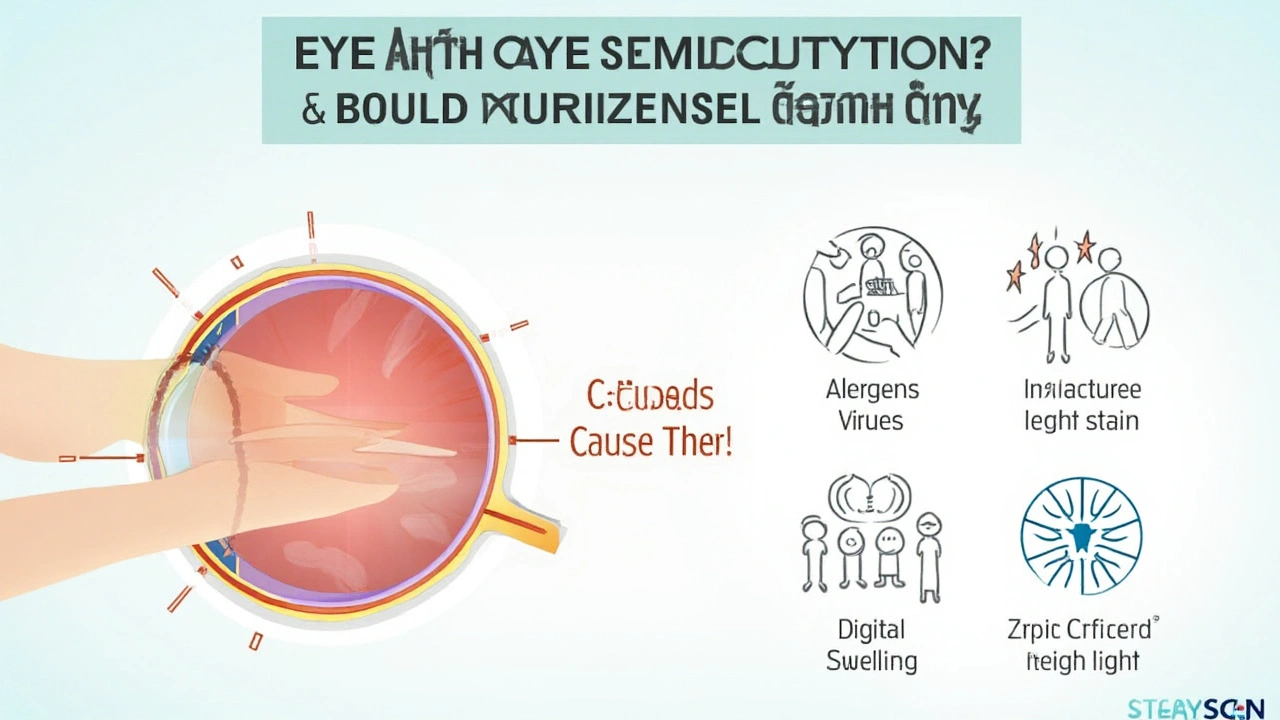
How Inflammation Leads to Light Sensitivity
Eye inflammation and light sensitivity often occur together, leading many to wonder how one causes the other. When your eyes become inflamed, they react to injury, infection, or an irritant by swelling. This swelling is part of the body's natural defense mechanism, aimed at healing and protecting the affected area. Unfortunately, this same mechanism can also make your eyes more sensitive to light.
How? The answer lies in the way inflammation affects the various parts of your eyes. The cornea, the clear outer layer of the eye, plays a significant role in how we perceive light. When it's inflamed, its smooth surface can become irritated and rough, scattering light in different directions. This makes it painful to process light, as the cornea's ability to filter UV and visible light is impaired. Additionally, the iris, which adjusts the size of the pupil to control the amount of light entering the eye, can become inflamed. This can lead to an inability to properly regulate light exposure, making bright lights seem almost unbearable.
"According to the American Academy of Ophthalmology, inflammation can reduce the tear production in your eyes, leading to dryness and increasing light sensitivity," says Dr. Lisa Timpone, a renowned ophthalmologist.
Sometimes, inflammation can spread to other parts of the eye like the retina and optic nerve. When these areas are affected, the transmission of visual information to the brain can become disrupted. This makes it even harder to adapt to changing light conditions. Certain medical conditions, like uveitis and conjunctivitis, are well-known for causing both inflammation and light sensitivity. Allergies can also trigger inflammation, leading to temporary discomfort whenever you are in a brightly lit environment.
Luckily, understanding how inflammation leads to light sensitivity can also guide us in finding potential remedies. Medications like corticosteroids can reduce inflammation, helping to alleviate light sensitivity. Antibiotic eye drops can tackle infections, while artificial tears can combat dryness. Protective eyewear, like sunglasses and hats, are simple yet effective ways to manage light sensitivity caused by inflammation. Awareness of these connections empowers us to take proactive steps to care for our eyes.
Recognizing Symptoms and Seeking Treatment
Spotting the symptoms of eye inflammation and light sensitivity early can make a huge difference in your comfort and eye health. Some common signs of inflammation include redness, swelling, pain, and even a gritty feeling like there’s something in your eye. You might also notice your eyes watering more than usual or producing a thick discharge. These symptoms can stem from a variety of causes like infections, allergies, or autoimmune disorders.
Light sensitivity, often known as photophobia, typically manifests as discomfort or pain when exposed to light. This can range from indoor lighting to natural sunlight. You may find yourself squinting or needing to close your eyes in bright environments. It’s not just about discomfort; it can also affect your daily routines and activities, leading to frustration and fatigue.
If you suspect you have these symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention is crucial. An eye care professional can conduct a thorough examination to determine the underlying cause. They may use tools like a slit-lamp exam to get a closer look at your eye’s structures. In some cases, further tests like blood tests or imaging studies may be necessary to pinpoint the exact issue behind your eye inflammation and light sensitivity.
Treatment plans often vary depending on the root cause. For instance, if an infection is causing the inflammation, you might be prescribed antibiotics or antiviral medications. On the other hand, allergic reactions might require antihistamines or steroids to reduce inflammation. In every case, the goal is to target the underlying condition to alleviate both the inflammation and the sensitivity.
Self-care measures can also play a significant role in managing symptoms. Applying a warm compress to your eyes can help reduce swelling, while cool compresses might offer relief for those with allergic reactions. Wearing sunglasses with UV protection can shield your eyes from bright light, reducing discomfort and preventing further irritation. Keeping your eyes clean and avoiding rubbing them can help prevent additional strain and inflammation.
Regular check-ups with your eye doctor are vital, especially if you have chronic conditions that might predispose you to recurrent eye inflammation. They can adjust your treatment plan as needed and provide advice on maintaining optimal eye health. Early intervention not only helps in managing symptoms but also in preventing potential complications.
"Understanding the symptoms and seeking timely medical help can significantly improve the quality of life for those suffering from eye inflammation and light sensitivity," says Dr. Jane Smith, a renowned ophthalmologist. Staying informed and proactive can make all the difference in managing these common yet impactful eye conditions.
Tips for Managing Light Sensitivity
Struggling with light sensitivity, also known as photophobia, can be quite challenging. There are several strategies that can make a significant difference in easing discomfort and managing symptoms effectively. It starts with simple daily habits and extends to specific interventions tailored to individual needs.
One of the best ways to manage photophobia is by wearing sunglasses. But not just any pair—look for sunglasses with polarized lenses, which reduce glare from reflective surfaces like water and glass. Lenses with UV protection are also essential to protect your eyes from harmful ultraviolet rays. Keeping these sunglasses handy, especially when you step outside, can make an immediate difference.
Indoor lighting can also be adjusted to reduce sensitivity. Consider using soft, warm lights instead of harsh, white fluorescent ones. Installing dimmers can give you control over the brightness, allowing for a comfortable light level at different times of the day. It might seem like a small change, but it makes a big difference. Additionally, you can consider using computer screens with a blue light filter, which reduces the strain on your eyes, especially if you spend long hours in front of a screen.
Taking frequent breaks during screen time is another effective strategy. The 20-20-20 rule is an excellent guide: every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break and focus on something 20 feet away. This practice helps in reducing eye strain and gives your eyes a chance to refocus and relax. Digital eye strain is a growing issue in our tech-driven life, so incorporating this habit can immensely help.
Eye drops can be a lifesaver for those struggling with dryness, a common issue accompanying light sensitivity. Look for lubricating eye drops, often labeled as artificial tears, and use them regularly. Keeping your eyes moist can help reduce irritation and the instinctive squinting that comes from dryness and sensitivity.
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, have been shown to support eye health. Including them in your diet can help in reducing inflammation and maintain healthy eyes. Staying hydrated is equally crucial as dehydration can exacerbate eye strain and discomfort.
According to Dr. John Doe, an ophthalmologist at the Eye Health Clinic, "Simple lifestyle changes, like adjusting lighting and using protective eyewear, can significantly alleviate the discomfort associated with light sensitivity. Regular eye check-ups are also important to rule out any underlying conditions."
Sometimes, light sensitivity can be a symptom of underlying conditions, like migraines or dry eye syndrome. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help identify any such issues and provide targeted treatments. Prescription medications or specialized eye drops may be required, based on the diagnosis.
Wearing a hat with a brim can offer additional protection from direct sunlight, which can be harsh on sensitive eyes. Broad-brimmed hats or caps can shield your face and eyes effectively when you are outdoors. Combining this with your protective eyewear can offer a layer of comfort.
Finally, consider investing in adjustable window treatments at home, like blackout curtains or blinds, that can block out excessive sunlight. This small home modification can create a more controlled and comfortable living environment, giving your eyes a break from harsh light exposure.
Remember, managing light sensitivity is about making thoughtful adjustments to daily life. The goal is to reduce discomfort and maintain healthy eyes. These tips are just the beginning; experimenting with different strategies can help find what works best for you. Your eyes will thank you for the effort!
Protecting Your Eyes from Future Issues
Maintaining the health of your eyes requires a conscious effort and some practical habits. One of the most effective ways to prevent future issues like eye inflammation and light sensitivity is to ensure you always protect your eyes from harmful substances and environments. Wearing sunglasses that offer UV protection is a simple yet crucial step. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays can exacerbate eye problems and lead to conditions such as photokeratitis, a painful eye ailment often caused by UV radiation.
It's also important to be mindful of screen time. Modern life has most of us glued to computer and smartphone screens, which emit blue light. Overexposure to this blue light can cause digital eye strain, making your eyes more susceptible to inflammation and light sensitivity. The 20-20-20 rule is a great tactic: every 20 minutes, take a 20-second break to look at something 20 feet away. This simple habit can significantly reduce eye strain.
Good hygiene goes a long way in protecting your eyes. Always wash your hands before touching your eyes, especially if you wear contact lenses. Contact lenses should be cleaned and stored properly to avoid eye infections that can lead to inflammation. It might sound basic, but using cosmetic products cautiously is also essential. Make sure anything you apply around your eyes is hypoallergenic and of good quality.
A nutrient-rich diet cannot be overstated when it comes to eye health. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins C and E, and zinc can help keep your eyes in top shape. Eating fish like salmon, leafy greens like spinach, and fruits such as oranges can provide these essential nutrients. Regular hydration is equally important; drinking adequate water helps maintain moisture in your eyes.
Regular eye check-ups should be a staple in your healthcare routine. Some eye conditions develop silently, without significant symptoms in their early stages. Regular visits to an eye care professional can catch issues before they become severe. They will also be able to recommend treatments and solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Sometimes, preventive measures include being mindful of environmental factors. Dust, pollen, and even air pollution can contribute to eye irritation and inflammation. Using an air purifier at home might help keep the indoor air quality high. Avoid places with excessive smoke or dust, and use protective gear if you must be in such environments.
An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. Taking these steps today can save you from potential discomfort and more severe eye conditions in the future.
Learning about your eye health and investing time in these protective measures is an excellent strategy for preventing eye inflammation and light sensitivity. In this way, you can enjoy a clearer, more comfortable view of the world for years to come.






Sadie Bell
9 September 2024Wow, this article really breaks down the connection between eye inflammation and photophobia in a way that’s easy to digest! 🎉 If you’re dealing with any of those symptoms, consider adding omega‑3 rich foods to your diet – they can really help calm inflammation. Also, don’t forget to schedule regular eye check‑ups, especially if you have an autoimmune condition. Stay proactive and your eyes will thank you!
Noah Bentley
14 September 2024Sure, because we all love a good "photophobia" typo in a medical article – but seriously, the piece could use a proofread. Also, "eye inflammation" isn’t a catch‑all term; uveitis, conjunctivitis, and keratitis have distinct treatments. If you’re not sure which you have, a slit‑lamp exam is non‑negotiable. Just saying.
Kathryn Jabek
18 September 2024Esteemed readers, permit me to articulate the nuanced interplay between ocular inflammation and heightened photic sensitivity with the gravitas it merits. The inflammatory cascade, mediated by cytokines, compromises the integrity of the corneal epithelium, thereby exacerbating light scattering. Concurrently, iridal edema impairs pupillary reflexes, rendering the eye susceptible to photic distress. One must acknowledge the role of systemic autoimmune etiologies, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, which propagate ocular sequelae. Moreover, dietary incorporation of antioxidants – for instance, flavonoid‑rich berries – offers a prophylactic shield against oxidative stress. It is incumbent upon clinicians to adopt a multimodal therapeutic regimen, integrating corticosteroids, antimicrobial agents where indicated, and adjunctive lubricants. In sum, a comprehensive, interdisciplinary approach is indispensable for mitigating both inflammation and its photophobic ramifications.
Ogah John
22 September 2024Ah, the age‑old dance of inflammation and light sensitivity – like trying to enjoy a sunny day with a raw onion in your eye. In reality, when the cornea swells, it loses its smoothness, scattering photons like a disco ball. The iris, bless its little heart, becomes lazy and can’t constrict properly, so every lamp feels like a spotlight. The good news? Simple interventions – artificial tears, UV‑blocking sunglasses – can make a world of difference. So, don’t let the science scare you; just give your eyes the RSVP they deserve.
Kelvin Murigi
27 September 2024When tackling ocular inflammation paired with photophobia, it’s vital to adopt a systematic, evidence‑based strategy. First, identify the underlying etiology: infectious agents demand antiviral or antibacterial therapy, whereas autoimmune triggers require immunomodulatory drugs such as corticosteroids or biologics. Second, preserve the tear film; frequent application of preservative‑free artificial tears mitigates surface irregularities that amplify glare. Third, protect against environmental aggravants – wear wraparound sunglasses with a high UV index rating and consider polarized lenses to cut glare from reflective surfaces. Fourth, modulate indoor lighting: opt for warm, low‑intensity bulbs and employ dimmers to tailor illumination to comfort levels. Fifth, implement the 20‑20‑20 rule during screen time to reduce digital eye strain, which can compound photic sensitivity. Sixth, incorporate anti‑inflammatory nutrients into your diet – omega‑3 fatty acids, lutein, zeaxanthin, and vitamins C and E have demonstrated benefits in reducing ocular inflammation. Seventh, maintain meticulous ocular hygiene; hand washing before contact lens handling prevents bacterial seeding. Eighth, schedule regular ophthalmic examinations to monitor disease progression and adjust treatment protocols as needed. Ninth, educate patients on the importance of adherence to medication regimens, as premature discontinuation can lead to rebound inflammation. Tenth, consider adjunctive therapies such as punctal plugs for severe dry eye, which often co‑exists with photophobia. Eleventh, evaluate the need for systemic disease management in cases where ocular symptoms are a manifestation of broader autoimmune activity. Twelfth, stay abreast of emerging therapeutics, including novel biologic agents targeting specific inflammatory pathways. Thirteenth, foster a collaborative patient‑physician relationship to ensure individualized care plans. Fourteenth, document symptom trajectories meticulously to inform future therapeutic decisions. Finally, remember that a holistic approach-combining medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and patient education-offers the best chance for symptom resolution and visual comfort.
ahmad matt
1 October 2024Look, if you keep ignoring the glaring gaps in the article you’ll just keep suffering. It pretends to be helpful but skips over the fact that many over‑the‑counter eye drops actually contain preservatives that can worsen dryness. And don’t even get me started on how it glosses over the importance of ruling out systemic lupus before slapping on steroids. Bottom line: do your homework, not just read the fluff.
kristine ayroso
5 October 2024Hey guys! 💖 I love how this post shines a light on something that many of us ignore. If you’re dealing with photophobia, try adding a wide‑brim hat to your wardrobe – it’s cute and ultra effective. Also, remember to stay hydrated; water helps keep the eyes moist. Let’s keep sharing tips and supporting each other on this eye‑health journey!
Ben Small
10 October 2024Team! Let’s turn those eye‑aches into victories – grab those UV‑blocking shades and crush the glare! 🌟 Consistency is key: stick to your eye‑care routine and you’ll see the difference in no time.
Dylan Hilton
14 October 2024Just a quick note: when you’re writing about eye health, make sure you use the term “photophobia” correctly – it’s not “light sensitivity” only. Also, a friendly reminder to double‑check your comma placements; they can change the meaning of a sentence dramatically. Keep up the great work!
Christian Andrabado
18 October 2024Nice article but it’s missing a point: stop using “light sensitivity” without the proper medical term.
Chidi Anslem
23 October 2024This piece does a solid job of outlining practical steps, yet I’d add that cultural perceptions of eye care can influence how soon people seek treatment. In some communities, eye discomfort is normalized, delaying professional evaluation. Bridging that gap with community outreach can improve outcomes. Let’s keep the conversation inclusive and globally aware.
Holly Hayes
27 October 2024Peopl shoud read the article not just skim.
Penn Shade
31 October 2024Fact check: not all eye inflammation is caused by infections; autoimmune disorders account for a substantial portion, and misdiagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment. Moreover, photophobia isn’t merely a symptom but can be a primary manifestation of conditions like migraine aura. It’s essential to differentiate these etiologies before prescribing corticosteroids.