QTc Interval: What It Is, Why It Matters, and Which Medications Affect It
When your heart beats, it goes through a cycle of electrical signals that make the muscles contract and relax. The QTc interval, a corrected measurement of the time between the start of the Q wave and the end of the T wave on an ECG, reflecting how long the heart’s ventricles take to electrically reset after each beat. Also known as corrected QT interval, it’s a simple number—but one that can mean the difference between a safe medication and a life-threatening rhythm problem. If your QTc interval gets too long, your heart can slip into a dangerous rhythm called torsades de pointes, which can lead to sudden cardiac arrest. It’s not something you feel, but doctors check it all the time—especially when you’re on certain drugs.
Many common medications can stretch the QTc interval, even if they’re not heart drugs. Antipsychotics like clozapine and loxapine are well-known culprits. So are some antidepressants like amitriptyline. Even antibiotics, anti-nausea meds, and certain antifungals can do it. That’s why your doctor might order an ECG before starting you on one of these. It’s not overcaution—it’s prevention. The same goes for people with existing heart conditions, low potassium or magnesium, or those taking multiple meds at once. Polypharmacy doesn’t just mean more pills—it means more chances for hidden risks.
It’s not just about the drug itself. Your body’s metabolism plays a role too. Some drugs, like those affected by CYP1A2 or CYP3A4 enzymes, can interact with others and change how quickly they clear from your system. That’s why charcoal-grilled meats or pomegranate juice might seem harmless—but in the wrong mix, they can push a borderline QTc into danger. Even something as simple as skipping a meal or getting dehydrated can lower your electrolytes and make your heart more vulnerable.
Knowing your QTc isn’t about fear. It’s about awareness. If you’re on any psychiatric, cardiac, or chronic pain medication, ask if your QTc has been checked. If you’ve ever had an unexplained fainting spell, dizziness, or irregular heartbeat, bring it up. Most of the time, nothing’s wrong. But when something is, catching it early saves lives. Below, you’ll find real-world guides on the meds that affect this interval, how to spot the risks, and what to do if you’re already on one of them.
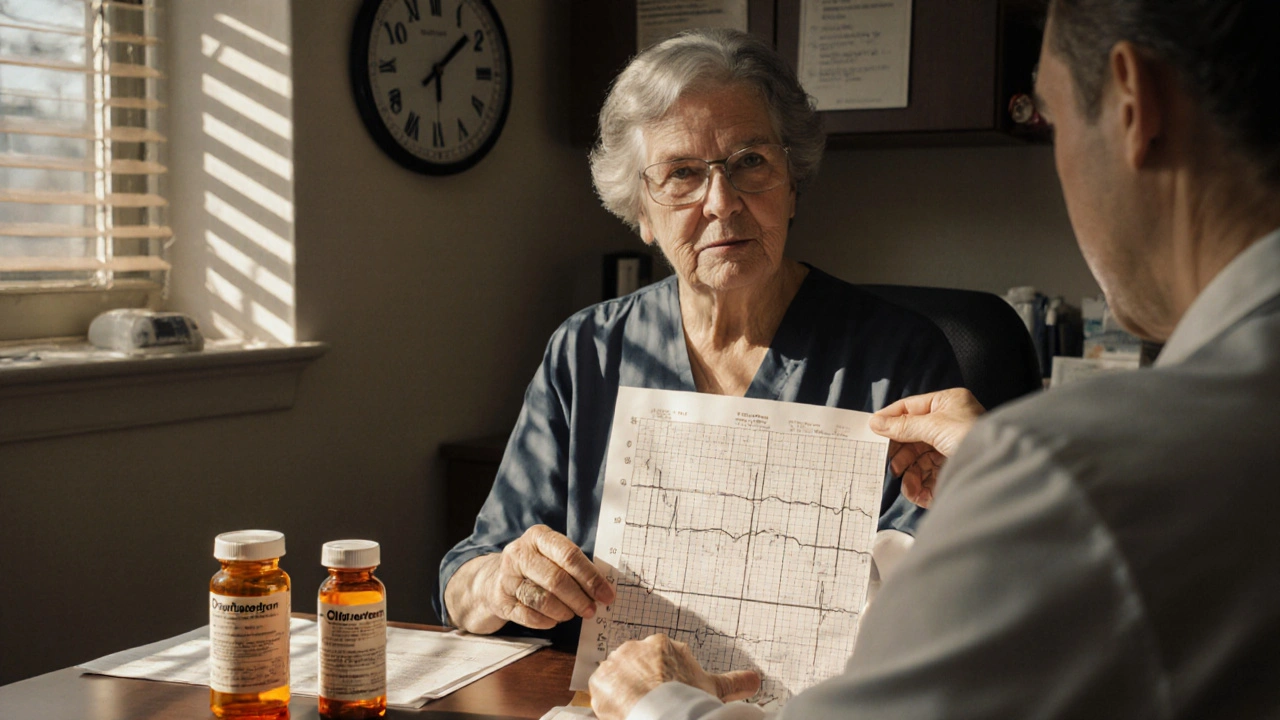

QT Prolongation: Medications That Raise Arrhythmia Risk
QT prolongation can trigger deadly heart rhythms like torsades de pointes. Over 220 medications, from antibiotics to antidepressants, carry this risk. Know which ones to watch for and how to stay safe.
MedicationsLatest Posts
Tags
- online pharmacy
- medication safety
- generic drugs
- medication
- dietary supplement
- side effects
- online pharmacy UK
- drug interactions
- mental health
- impact
- online pharmacies
- statin side effects
- dosage
- adverse drug reactions
- generic vs brand
- pediatric antibiotics
- antibiotic side effects
- FDA drug safety
- skin health
- health